Wound healing is a complex process that is essential for tissue repair after injury, surgery or illness. Although the human body has a remarkable capacity for self-healing, certain factors, such as age, chronic illness or infection, can slow down this process. In recent years, alternative methods, such as magnet therapy, have attracted growing interest for their ability to support and accelerate healing. But how does it work? And is it really effective?
Understanding the healing process
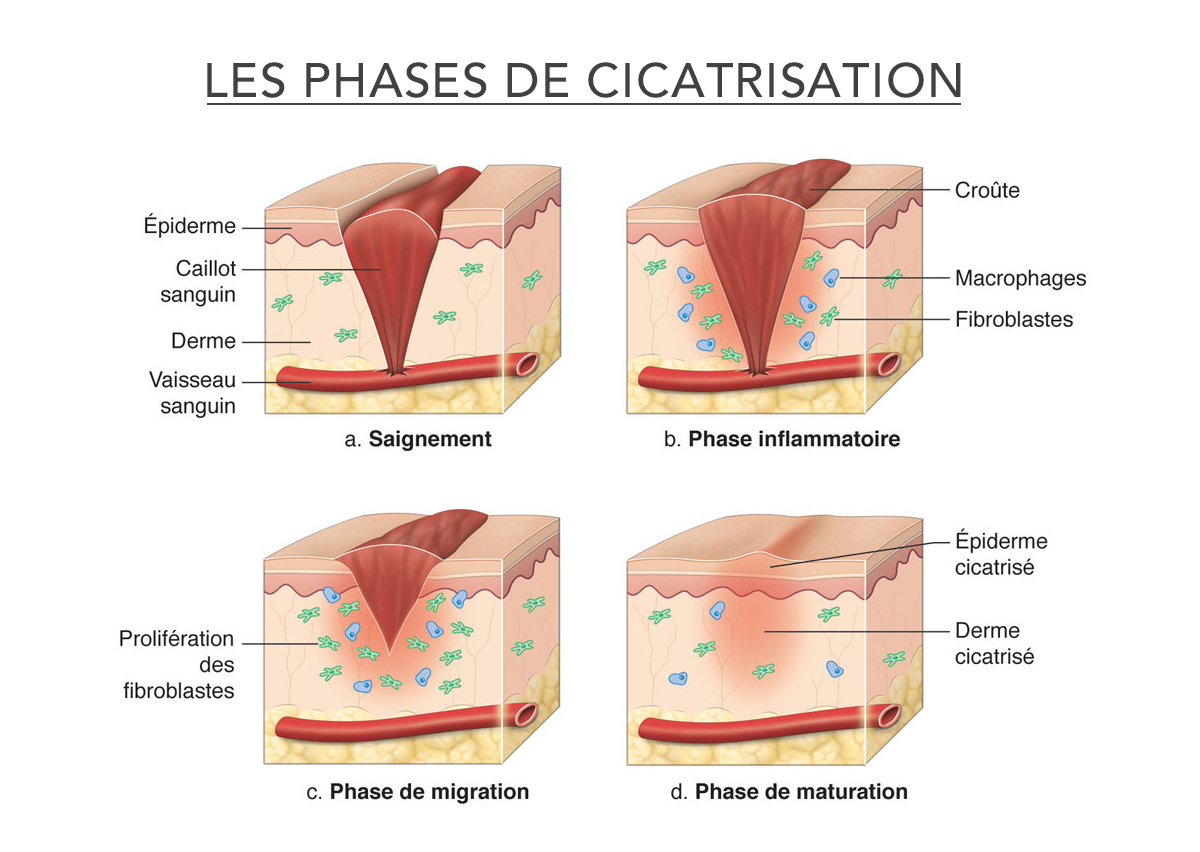
Wound healing is a complex biological mechanism, divided into three main phases:
- Inflammatory phase (0 to 3 days): after an injury, the body triggers inflammation to eliminate bacteria and debris. The blood vessels dilate to allow the influx of white blood cells and platelets.
- Proliferation phase (3 to 20 days): fibroblasts (repair cells) produce collagen to rebuild the damaged tissue. The blood vessels regenerate, and new skin begins to form.
- Maturation phase (21 days to several months): the collagen is reorganised to strengthen the healed area. The wound becomes stronger and less visible.
Factors such as poor blood circulation, infection or a lack of nutrients can disrupt these stages, resulting in more significant scarring or delayed healing.
The challenges associated with slow healing
Some people are particularly prone to healing problems:
- Older people: with age, the skin loses its elasticity and blood circulation decreases, delaying healing.
- People with diabetes: diabetes can damage blood vessels, making healing more difficult.
- Smokers: tobacco reduces the supply of oxygen to the tissues, which disrupts the process.
- People with weakened immune systems: their bodies react less effectively to infections and injuries.
In these cases, complementary approaches such as magnet therapy can play a significant role.
Magnet therapy: an ally for healing
Magnet therapy is a technique based on the use of magnetic fields to stimulate the body's natural mechanisms. It can take different forms: magnets worn on the skin, devices generating pulsed magnetic fields or magnetically active textiles.
How does it affect healing?
1. Improved blood circulation:
Magnetic fields stimulate blood flow in the affected area, increasing the supply of oxygen and nutrients essential for tissue repair.
2. Reduction of inflammation:
Magnetic fields help regulate the activity of white blood cells, thus reducing swelling and pain. This promotes a faster transition to the proliferation phase.
3. Analgesic effect:
By reducing pain, magnet therapy can improve comfort and allow for better mobility, which is crucial to avoid complications related to immobility.
Scientific studies and testimonials
Numerous studies explore the effects of magnetotherapy on healing:
- Research published in the Journal of Wound Care has shown that the use of pulsed magnetic fields on chronic wounds can accelerate healing and reduce pain in diabetic patients.
- Another study, conducted on superficial burns, revealed that patients using magnets had a significant reduction in healing time compared to a control group.
Many users also report positive results: faster healing, reduced inflammation and associated pain.
Precautions and limitations
Although magnet therapy is generally considered safe, a few precautions should be taken:
- It is contraindicated for people with pacemakers or other implanted electronic devices.
- In the event of an active infection, it is important to consult a doctor for appropriate treatment before using magnet therapy.
A promising tool for healing
Magnet therapy is a gentle and effective method to support the healing process. By improving circulation, reducing inflammation and stimulating cell regeneration, it can offer valuable support, especially for people with difficult healing.