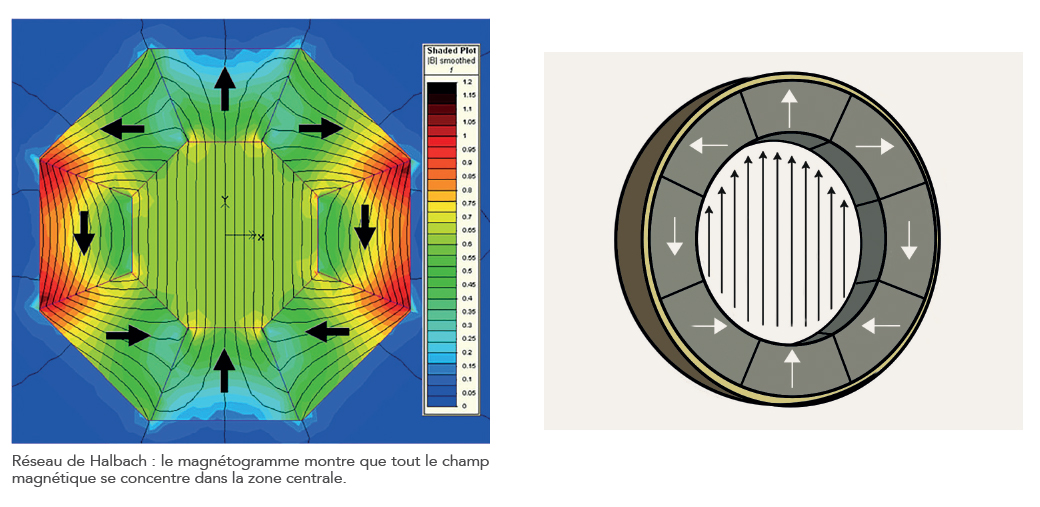
This is an astonishing magnetic system called “Halbach’s network” or “magic cylinder”. This assembly of magnets creates a dense and homogeneous magnetic field in its center. This device is used for example in MRI to create a strong uniform magnetic field in the examination area.
The Halbach cylinder consists of magnets in the shape of trapezoidal segments, 8 in this example. In each segment the magnetisation vector is constant. From one segment to the next, the magnetisation rotates 90 degrees each time. The magnetic field thus created inside the cylinder is approximately constant in intensity and direction. It is confined to the inside of the cylinder, without leakage to the outside. It is therefore particularly high, about 2 Tesla with neodymium
magnets.
Its name comes from physicist Klaus Halbach, who worked at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory during the 80s, and invented the device to focus the beams of particle accelerators.